An often-overlooked advantage of using Power BI and Excel together is the ability to connect Excel to Power BI datasets. This technique gives Excel users and Power BI developers the flexibility to provide managers with reports they’re familiar with without having to publish two separate reports.
Table of Contents
The Benefits of Connect Excel to Power BI Datasets
There are a number of benefits of connecting Excel to Power BI. The biggest one being Power BI’s more modern feature set. Microsoft heavily invests in adding new features to Power BI on a monthly basis, while Excel is a mature product with minimal ongoing investment. Fortunately, you can leverage both systems by connecting them together.
Here are some of the benefits of establishing a connection between Excel and Power BI.
- Enable Automatic Data Refreshes using the Power BI Service
- Pivot Tables are more familiar to many business users than Power BI Dashboards
- Leverage the Power BI Gateway to access on premises data
- Easily format data in views that finance and accountants are used to
- Power BI has more modern features than Excel Power Query or Get and Transform
Connect Excel to Power BI Using Analyze in Excel
The fastest way to connect Excel to Power BI is by using the built in Analyze in Excel feature. Navigate to a published Power BI report on PowerBI.com and then click on Export > Analyze in Excel. After a few moments a new Excel file will be generated with a pre-made pivot table that includes all fields available in the underlying Power BI dataset.
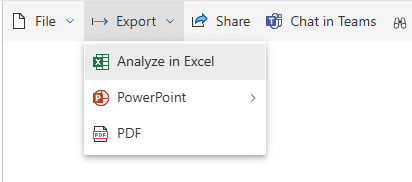
The amount of Power BI data available in the Excel Pivot Table is not limited to fields and columns that are being used to populate visuals. This feature gives you access to all data that you have access to as a user, subject to Row Level Security (RLS).

When Row Level Security is not in use this feature gives people the ability to view data that they may not normally have access to see. Because of this, many Power BI Tenant Admins disable the option. If it does not exist in your instance of Power BI check with your company’s Power BI Administrator.
Connecting to Power BI Data from Excel
To connect Microsoft Excel to a Power BI Dataset, publish a dataset to the Power BI Service. Next, open Excel and click Insert > Pivot Table > From Power BI and select the published Power BI Dataset. You must be using the same Microsoft Account in Excel that has access to the Power BI dataset. Once connected, a Pivot Table will appear where you can work with connected Power BI data.
Here’s how in more detail.
Step 1.) Pre-Requisites for Connecting Excel to Power BI
Prior to starting, make sure that you are both logged into PowerBI.com and Excel using the same account. This determines which Power BI datasets you have access to. Also ensure that you have an up-to-date version of Excel Desktop installed. This feature is not supported on older versions.
If you follow these instructions and the option is still not available reach out to your corporate Power BI admin to have them enable live connections. Your tenant of Power BI must have live connections enabled for Power BI.
Step 2.) Insert a Pivot Table
From Excel, go to the Insert Table and select Pivot Table, From Power BI. A list of available Power BI Datasets will appear in a panel to the right of Excel.
If this option is not visible for you, make sure that you are logged in to Excel under the correct Microsoft account. If you update it, close Excel and re-open it. The connect to Power BI option should appear.

Once you select From Power BI, you will have Power BI Dataset pane that opens up on the right side of Microsoft Excel.
Step 3.) Select a Power BI Dataset
Once you find the dataset that you want to use for your pivot table click on + Insert Pivot Table.
This will create a pivot table in the existing worksheet.

You can interact and use the pivot table the same as you would with any other pivot table, including formatting, totals, and calculated fields. It may take a second or two to update each time you change the Pivot Table. Excel queries the Power BI Dataset for each change.
If you prefer to not work with Power BI data in a Pivot Table, you can also Export Data from Power BI to Excel
